GENETIC DIVERSITY OF NATURALLY DISTRIBUTED Rhododendron moulmainense Hook. f. POPULATIONS IN LAM VIEN PLATEAU, VIETNAM REVEALED BY ISSR AND SCoT MARKERS
11.03.2021 -
GENETIC DIVERSITY OF NATURALLY DISTRIBUTED Rhododendron moulmainense Hook. f. POPULATIONS IN LAM VIEN PLATEAU, VIETNAM REVEALED BY ISSR AND SCoT MARKERS
Luu The Trung1, La Anh Duong2, Tran Van Tien3, Le Ngoc Trieu3 và Phi Hông Hai2*
1Forest Science Institute of central Highlands and South of central Viet Nam
2Vietnamese Academy of Forest Science
3Faculty of Biology, Dalat University
Abstract
Genetic diversity and variation of three naturally distributed Rhododendron moulmainense populations in the Lam Vien Plateau of Vietnam were analyzed using ISSR and ScoT markers separately and data from the two types of markers were then combined to show the overall results. Based on combined data, the genetic diversity parameters of the Tuyen Lam population were percentage of polymorphic bands (PPB) = 28.79%; genetic heterozygosity (He) = 0.1041; Shannon index (I) = 0.1552. The corresponding parameters were PPB = 37.88%; He = 0.1434; I = 0.2131 in the Hon Nga population, and PPB = 46.21%; He = 0.1857; I = 0.2709 in the Bidoup population. At the species level in Lam Dong province, the corresponding parameters were PPB = 62.12%; He = 0.1747; I = 0.2756. The average of pairwise genetic similarity coefficients among investigated individuals of Tuyen Lam population was 0.973, of Hon Nga population was 0.911, and of Bidoup population was 0.895. The genetic differentiation and the number of migrants per generation among investigated populations were GSTS = 0.1735 and Nm = 2.3824 individuals, respectively. Genetic distance between Tuyen Lam and Hon Nga populations was 0.0399, between Tuyen Lam and Bidoup populations were 0.0621, and Bidoup and Hon Nga populations were 0.0670. Data generated by both marker types and the combined revealed similar trends of genetic diversity levels among the studied populations. The SCoT data showed higher values of genetic diversity and population gene differentiation than did the ISSR data, but the latter showed higher gene differentiation among sampled individuals in the study populations. Comparing the values of Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) for discriminatory ability; Effective Multiplex Ratio (EMR) for several revealed loci and/or efficiency of the primer-marker system; Marker Index (MI) for the efficiency of used method; and Resolving Power (Rp) between used techniques indicated that discriminatory ability, efficiency, and ability of the ISSR primer combinations were higher but using ScoT marker system was more efficient than ISSR marker system for evaluating genetic diversity.
Key words: Rhododendron moulmainense, ISSR, SCoT genetic diversity, Vietnam
Sources: Malays. Appl. Biol. (2020) 49(5): 41–52
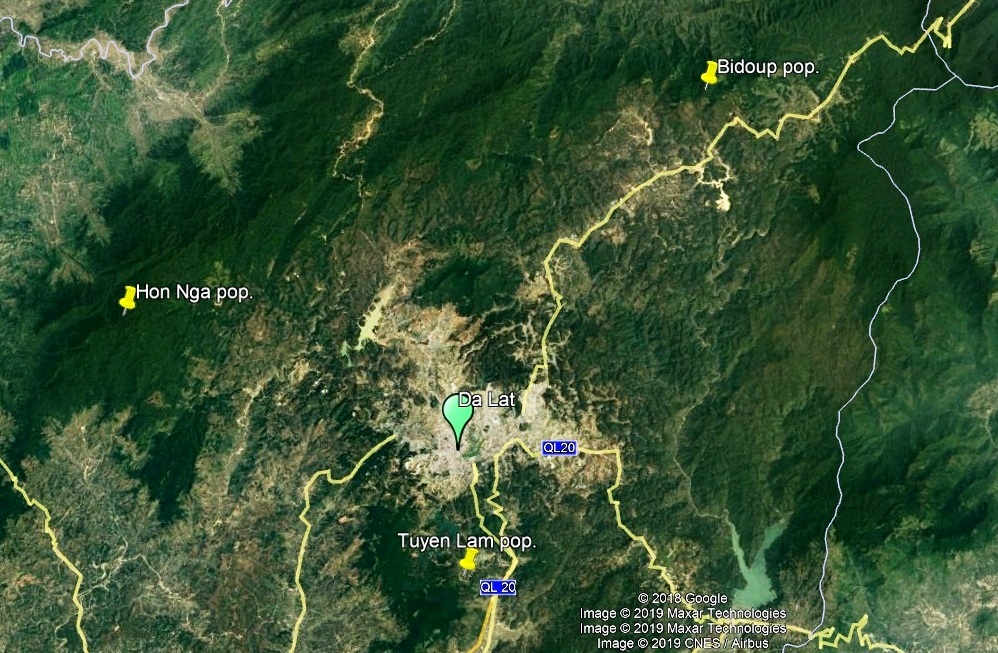
Fig. 3. Distribution of three investigated R. moulmainense populations
-
Species-Specific Allometric Equations for Predicting Belowground Root Biomass in Plantations: Case Study of Spotted Gums (CORYMBIA citriodora subspecies variegata) in Queensland
16.09.2021 -
Respiratory temperature responses of tropical conifers differ with leaf morphology
08.09.2021 -
Sinh trưởng và ảnh hưởng của các nhân tố sinh thái đến sinh trưởng rừng trồng thông Caribê (Pinus caribaea Morelet) tại Lâm Đồng
07.09.2021 -
Buổi lễ công bố trao quyết định Quyền Viện trưởng Viện Khoa học Lâm nghiệp Nam Trung Bộ và Tây Nguyên
11.08.2021 -
Buổi gặp mặt chia tay và trao quyết định nghỉ hưu.
11.08.2021 -
Ảnh hưởng của chất điều hòa sinh trưởng thưc vật lên hom cành dum tuyết (Rubus niveus) trong điều kiện nhà kính tại Đà Lạt
24.03.2021 -
Field methods for above and belowground biomass estimation in plantation forests
23.03.2021 -
GENETIC DIVERSITY OF NATURALLY DISTRIBUTED Rhododendron moulmainense Hook. f. POPULATIONS IN LAM VIEN PLATEAU, VIETNAM REVEALED BY ISSR AND SCoT MARKERS
11.03.2021
